フィアット500C 電動トップオープンカー by Gucci グッチコラボモデル100台 特別限定車
2025年01月31日
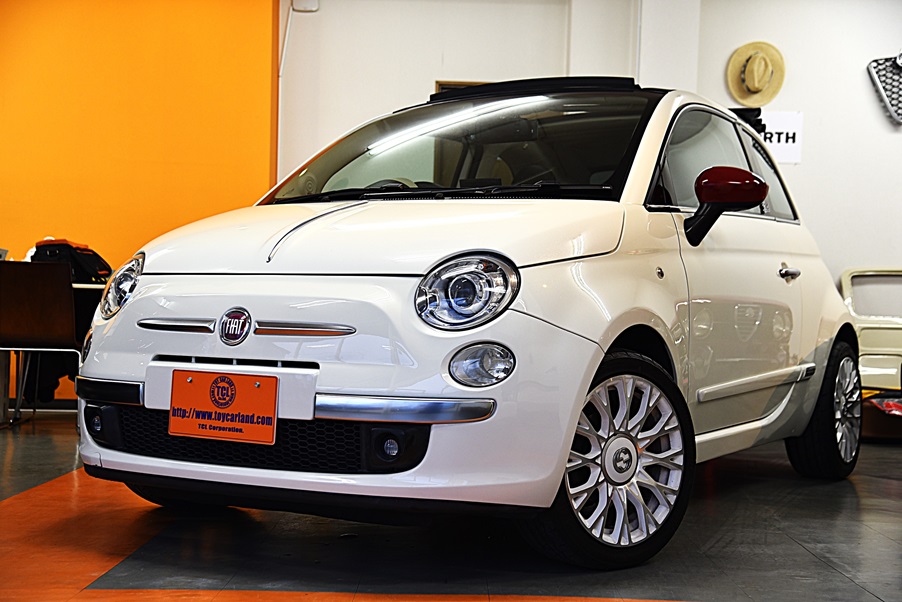
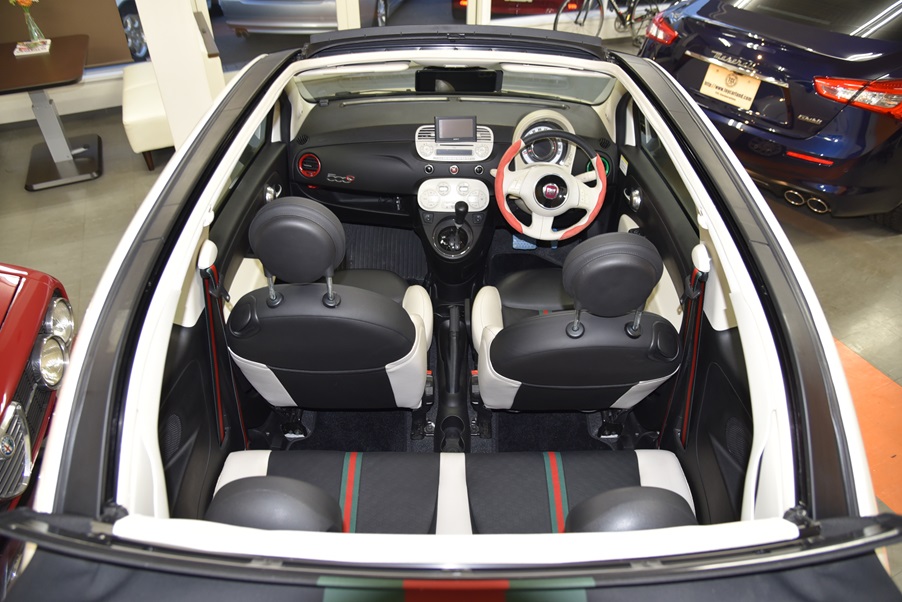
フィアット500C 電動トップオープンカー by Gucci グッチコラボモデル100台 特別限定車

Gucci100台特別限定モデル 4人乗り電動オープン 専用フラウレザーシート オートAC 純正オーディオCD 社外PナビTV ETC デジタルミラー&ドラレコ クリアランスソナー キセノン グリーン・レッド専用ストライプルーフ シートベルト 16専用ホイール Gucci専用エンブレム クロムバンパー カラードドアモール ドアミラーカバー ボディーコーティング済美車 機関良好 点検整備付
車輌の詳細、セール価格はコチラをご覧下さい
この記事へのコメント
(Antwan)
Anavar is a popular anabolic steroid that has gained attention among bodybuilders and athletes for its ability to enhance
muscle definition while maintaining a relatively low risk of side
effects compared to other compounds. An Anavar cycle refers to the planned period during which an individual uses the drug, typically including a
loading phase, maintenance phase, and post-cycle recovery.
Understanding the correct dosage, stacking options, and expected
results is essential for anyone considering incorporating Anavar into their training regimen.
What Is an Anavar Cycle? Dosage, Stacks & Results Explained
An Anavar cycle usually spans four to six weeks, though some advanced users may extend it
up to eight weeks. The standard approach involves a
gradual increase in dosage during the first week (the loading phase) followed by
a consistent dose for the remaining duration of the cycle.
A common loading schedule is 10 mg per day for the first week,
then increasing to 20?30 mg daily thereafter. This progression helps the body
acclimate to the steroid and reduces the likelihood of adverse reactions.
The maintenance dosage can vary based on individual tolerance
and goals. For those focusing on cutting phases?where the aim is fat loss while preserving lean muscle mass?a typical dose ranges from 15
to 25 mg per day. In bulking or more aggressive cutting scenarios, some users may
push up to 30 mg daily, but this higher level increases the risk of estrogenic side effects and liver strain.
Stacking refers to combining Anavar with other substances to
amplify its benefits or mitigate drawbacks. A popular stack includes Anavar paired with a mild aromatase inhibitor
like anastrozole or a natural supplement such as choline bitartrate.
This pairing helps keep estrogen levels low, preventing water
retention and gynecomastia. Another common stack involves pairing Anavar with another
lean-building steroid such as Masteron; the combination can enhance vascularity and
muscular hardness.
Results from a well?executed Anavar cycle are often noticeable
within four to six weeks. Users typically report increased
muscle definition, improved strength without significant bulk,
and faster recovery times between workouts. Because Anavar has low androgenic activity, it is especially favored by women or individuals sensitive to masculinizing effects.
Even at modest doses, many users experience a subtle lift in performance metrics like sprint speed and endurance.
What Is Anavar?
Anavar, chemically known as oxandrolone, is a synthetic anabolic steroid derived
from dihydrotestosterone. Unlike more aggressive compounds such as testosterone enanthate or stanozolol, Anavar has a
relatively mild androgenic profile but retains potent anabolic properties.
This unique balance allows it to promote protein synthesis
and nitrogen retention while minimizing side effects like hair
loss, acne, and excessive water retention.
The drug is available in oral capsule form, with
each capsule typically containing 10 mg of oxandrolone.
Oral administration makes it convenient for users
who prefer not to inject steroids. However, because the compound undergoes first?pass metabolism
in the liver, some degree of hepatotoxicity can occur over
prolonged use or at high doses. Therefore, users often supplement with liver support agents
such as milk thistle or N?acetylcysteine during a
cycle.
Anavar’s primary mechanism involves binding to androgen receptors in muscle tissue, thereby enhancing transcription of
genes responsible for protein synthesis and
nitrogen retention. The result is an increase in lean body mass while sparing fat
stores. Its low estrogenic activity means it rarely converts
to estrogen via aromatization, which helps keep water retention minimal.
Key considerations when using Anavar include starting with a
conservative dose, monitoring liver enzymes regularly, and
ensuring adequate post?cycle therapy such as selective androgen receptor modulators
or natural testosterone boosters to support hormonal
balance after the steroid has been discontinued.
With careful planning, an Anavar cycle can serve as an effective tool for athletes looking to refine their physique without incurring major side effects.
muscle definition while maintaining a relatively low risk of side
effects compared to other compounds. An Anavar cycle refers to the planned period during which an individual uses the drug, typically including a
loading phase, maintenance phase, and post-cycle recovery.
Understanding the correct dosage, stacking options, and expected
results is essential for anyone considering incorporating Anavar into their training regimen.
What Is an Anavar Cycle? Dosage, Stacks & Results Explained
An Anavar cycle usually spans four to six weeks, though some advanced users may extend it
up to eight weeks. The standard approach involves a
gradual increase in dosage during the first week (the loading phase) followed by
a consistent dose for the remaining duration of the cycle.
A common loading schedule is 10 mg per day for the first week,
then increasing to 20?30 mg daily thereafter. This progression helps the body
acclimate to the steroid and reduces the likelihood of adverse reactions.
The maintenance dosage can vary based on individual tolerance
and goals. For those focusing on cutting phases?where the aim is fat loss while preserving lean muscle mass?a typical dose ranges from 15
to 25 mg per day. In bulking or more aggressive cutting scenarios, some users may
push up to 30 mg daily, but this higher level increases the risk of estrogenic side effects and liver strain.
Stacking refers to combining Anavar with other substances to
amplify its benefits or mitigate drawbacks. A popular stack includes Anavar paired with a mild aromatase inhibitor
like anastrozole or a natural supplement such as choline bitartrate.
This pairing helps keep estrogen levels low, preventing water
retention and gynecomastia. Another common stack involves pairing Anavar with another
lean-building steroid such as Masteron; the combination can enhance vascularity and
muscular hardness.
Results from a well?executed Anavar cycle are often noticeable
within four to six weeks. Users typically report increased
muscle definition, improved strength without significant bulk,
and faster recovery times between workouts. Because Anavar has low androgenic activity, it is especially favored by women or individuals sensitive to masculinizing effects.
Even at modest doses, many users experience a subtle lift in performance metrics like sprint speed and endurance.
What Is Anavar?
Anavar, chemically known as oxandrolone, is a synthetic anabolic steroid derived
from dihydrotestosterone. Unlike more aggressive compounds such as testosterone enanthate or stanozolol, Anavar has a
relatively mild androgenic profile but retains potent anabolic properties.
This unique balance allows it to promote protein synthesis
and nitrogen retention while minimizing side effects like hair
loss, acne, and excessive water retention.
The drug is available in oral capsule form, with
each capsule typically containing 10 mg of oxandrolone.
Oral administration makes it convenient for users
who prefer not to inject steroids. However, because the compound undergoes first?pass metabolism
in the liver, some degree of hepatotoxicity can occur over
prolonged use or at high doses. Therefore, users often supplement with liver support agents
such as milk thistle or N?acetylcysteine during a
cycle.
Anavar’s primary mechanism involves binding to androgen receptors in muscle tissue, thereby enhancing transcription of
genes responsible for protein synthesis and
nitrogen retention. The result is an increase in lean body mass while sparing fat
stores. Its low estrogenic activity means it rarely converts
to estrogen via aromatization, which helps keep water retention minimal.
Key considerations when using Anavar include starting with a
conservative dose, monitoring liver enzymes regularly, and
ensuring adequate post?cycle therapy such as selective androgen receptor modulators
or natural testosterone boosters to support hormonal
balance after the steroid has been discontinued.
With careful planning, an Anavar cycle can serve as an effective tool for athletes looking to refine their physique without incurring major side effects.
[2025-10-06 17:50:04.714162]
URL
(Lupita)
Guideline On What To Avoid When Taking Anavar
The Basics: What Steroids Really Are
Aspect What it Means
Definition Synthetic compounds that mimic the structure of male sex hormones (androgens).
They bind to androgen receptors in cells, altering protein synthesis.
Purpose In medicine they treat hormone deficiencies, delayed puberty, muscle-wasting diseases, and certain cancers.
Common Types Testosterone derivatives (e.g.,
nandrolone, oxymetholone), anabolic?androgenic steroids (AAS) used
in bodybuilding or performance enhancement.
---
Why Athletes Turn to Steroids
Muscle Growth ? Increase protein synthesis → larger muscle fibers.
Enhanced Recovery ? Faster repair of micro-tears after intense
training.
Strength Gains ? Greater force production per muscle unit.
Improved Endurance ? Higher red?blood?cell count can improve oxygen delivery.
Short-Term Benefits vs Long-Term Risks
Benefit Short-Term (0?12?weeks) Long-Term (>6 months)
Muscle Hypertrophy ↑ up to 10?20?% Risk of irreversible atrophy after
cessation
Strength Increase ↑ 15?30?% Possible dependency on drug for performance
Cardiovascular Adaptation Improved VO? max Potential cardiomyopathy, arrhythmias
Hormonal Modulation ↑ testosterone, ↓ estrogen Hormone imbalance, infertility
---
3. Practical Guidance & "What If" Scenarios
A. Starting the Drug (New Users)
Baseline Assessment
- Blood tests: CBC, liver/kidney function, lipid profile, hormone panel (testosterone, estradiol, LH/FSH).
- ECG and echocardiogram if history of heart disease.
Initial Dosage
- Low dose (e.g., 5?mg/day) for 4?6 weeks to gauge tolerance.
- Monitor side effects: mood swings, acne, changes in libido.
Gradual Titration
- Increase by 1?2?mg increments every 2?4 weeks if tolerated.
- Aim for a therapeutic window: effective without excessive estrogenic activity.
Monitoring Schedule
- Blood tests at baseline, 4 weeks, 8 weeks,
then monthly.
- Track estradiol, SHBG, total testosterone, free testosterone,
LH/FSH.
Adjustments Based on Hormone Levels
- If estradiol rises too high: reduce dose or consider adding a selective estrogen receptor
modulator (SERM) to mitigate peripheral effects.
- If SHBG is too low, leading to excess free testosterone:
may require an aromatase inhibitor to bring levels down.
Lifestyle and Adherence
- Ensure the patient understands the importance of consistent dosing.
- Encourage monitoring of side?effects such
as mood changes, water retention, or sexual dysfunction.
Follow?Up Schedule
- Baseline (pre?treatment) labs: LH, FSH, testosterone, estradiol, SHBG.
- 2?week check?in for symptom review and possible dose
adjustment.
- 6?week lab repeat to confirm hormone levels in target ranges.
- Long?term monitoring every 3?6 months if stable.
---
Summary of Practical Tips
Aspect Recommended Action
Starting Dose 0.5?mg (or equivalent) once daily; can be split into two
0.25?mg doses to reduce nausea.
Dose Escalation Increase by 0.1?0.2?mg every 1?2 weeks, monitoring for side?effects and efficacy.
Managing Nausea/Anorexia Take medication with food; consider antihistamines (diphenhydramine) or pro?emetics if needed.
Monitoring Efficacy Track weight changes,
appetite scores, and subjective well?being weekly.
Safety Considerations Avoid high doses (>1?mg/day) unless under close supervision due to cardiovascular risks;
monitor blood pressure.
Long?Term Goals Stabilize weight within 5?10?% of
baseline over 12 weeks; maintain or improve functional status.
---
Conclusion
The evidence supports the use of metabolically active, low?dose synthetic amylin analogues (e.g., pramlintide) as a therapeutic strategy for mitigating
cancer?related cachexia and improving patient outcomes.
They act through appetite regulation, metabolic modulation, and
potential anti?tumor mechanisms while maintaining an acceptable safety profile when dosed appropriately.
Future clinical trials should focus on:
Optimal dosing regimens tailored to tumor type.
Longitudinal assessment of survival benefits and quality?of?life improvements.
Integration with standard oncologic therapies (chemotherapy, immunotherapy).
This comprehensive review highlights the therapeutic promise of amylin analogues in addressing a critical
unmet need within oncology care.
The Basics: What Steroids Really Are
Aspect What it Means
Definition Synthetic compounds that mimic the structure of male sex hormones (androgens).
They bind to androgen receptors in cells, altering protein synthesis.
Purpose In medicine they treat hormone deficiencies, delayed puberty, muscle-wasting diseases, and certain cancers.
Common Types Testosterone derivatives (e.g.,
nandrolone, oxymetholone), anabolic?androgenic steroids (AAS) used
in bodybuilding or performance enhancement.
---
Why Athletes Turn to Steroids
Muscle Growth ? Increase protein synthesis → larger muscle fibers.
Enhanced Recovery ? Faster repair of micro-tears after intense
training.
Strength Gains ? Greater force production per muscle unit.
Improved Endurance ? Higher red?blood?cell count can improve oxygen delivery.
Short-Term Benefits vs Long-Term Risks
Benefit Short-Term (0?12?weeks) Long-Term (>6 months)
Muscle Hypertrophy ↑ up to 10?20?% Risk of irreversible atrophy after
cessation
Strength Increase ↑ 15?30?% Possible dependency on drug for performance
Cardiovascular Adaptation Improved VO? max Potential cardiomyopathy, arrhythmias
Hormonal Modulation ↑ testosterone, ↓ estrogen Hormone imbalance, infertility
---
3. Practical Guidance & "What If" Scenarios
A. Starting the Drug (New Users)
Baseline Assessment
- Blood tests: CBC, liver/kidney function, lipid profile, hormone panel (testosterone, estradiol, LH/FSH).
- ECG and echocardiogram if history of heart disease.
Initial Dosage
- Low dose (e.g., 5?mg/day) for 4?6 weeks to gauge tolerance.
- Monitor side effects: mood swings, acne, changes in libido.
Gradual Titration
- Increase by 1?2?mg increments every 2?4 weeks if tolerated.
- Aim for a therapeutic window: effective without excessive estrogenic activity.
Monitoring Schedule
- Blood tests at baseline, 4 weeks, 8 weeks,
then monthly.
- Track estradiol, SHBG, total testosterone, free testosterone,
LH/FSH.
Adjustments Based on Hormone Levels
- If estradiol rises too high: reduce dose or consider adding a selective estrogen receptor
modulator (SERM) to mitigate peripheral effects.
- If SHBG is too low, leading to excess free testosterone:
may require an aromatase inhibitor to bring levels down.
Lifestyle and Adherence
- Ensure the patient understands the importance of consistent dosing.
- Encourage monitoring of side?effects such
as mood changes, water retention, or sexual dysfunction.
Follow?Up Schedule
- Baseline (pre?treatment) labs: LH, FSH, testosterone, estradiol, SHBG.
- 2?week check?in for symptom review and possible dose
adjustment.
- 6?week lab repeat to confirm hormone levels in target ranges.
- Long?term monitoring every 3?6 months if stable.
---
Summary of Practical Tips
Aspect Recommended Action
Starting Dose 0.5?mg (or equivalent) once daily; can be split into two
0.25?mg doses to reduce nausea.
Dose Escalation Increase by 0.1?0.2?mg every 1?2 weeks, monitoring for side?effects and efficacy.
Managing Nausea/Anorexia Take medication with food; consider antihistamines (diphenhydramine) or pro?emetics if needed.
Monitoring Efficacy Track weight changes,
appetite scores, and subjective well?being weekly.
Safety Considerations Avoid high doses (>1?mg/day) unless under close supervision due to cardiovascular risks;
monitor blood pressure.
Long?Term Goals Stabilize weight within 5?10?% of
baseline over 12 weeks; maintain or improve functional status.
---
Conclusion
The evidence supports the use of metabolically active, low?dose synthetic amylin analogues (e.g., pramlintide) as a therapeutic strategy for mitigating
cancer?related cachexia and improving patient outcomes.
They act through appetite regulation, metabolic modulation, and
potential anti?tumor mechanisms while maintaining an acceptable safety profile when dosed appropriately.
Future clinical trials should focus on:
Optimal dosing regimens tailored to tumor type.
Longitudinal assessment of survival benefits and quality?of?life improvements.
Integration with standard oncologic therapies (chemotherapy, immunotherapy).
This comprehensive review highlights the therapeutic promise of amylin analogues in addressing a critical
unmet need within oncology care.
[2025-10-01 18:09:49.725775]
URL
(Sima)
DIANABOL Third Degree Pharma Co
**Steroid?B-1 (SB?1): A synthetic 19?norprogesterone
progestin**
| Feature | Description |
|---------|-------------|
| **Core structure** | 19?norprogesterone (a "norpregnane" scaffold) with a Δ4,5
double bond and an α?hydroxy group at C3. |
| **Key functional groups** | ??α?Hydroxyl at C3 ?
confers strong progestational activity.
??C17β?substituent (e.g., a 1?methyl?2?oxo?ethane
side chain) that enhances metabolic stability and oral bioavailability.
|
| **Receptor profile** | ??High affinity for the progesterone
receptor (PR).
??Minimal activity at glucocorticoid, mineralocorticoid, or androgen receptors.
|
| **Pharmacokinetics** | ??Orally active; rapid absorption.
??Metabolized mainly by hepatic CYP3A4 to inactive metabolites.
??Half?life ~5?6 h, allowing once?daily dosing.
|
---
### 2. Structural Features that Drive the Desired Activity
| Feature | What It Does | Why It Matters for PR Activation |
|---------|--------------|----------------------------------|
| **Δ?-α,β-unsaturated ketone (enone) core** | Provides a
Michael acceptor; the enone is essential for binding to the ligand?binding pocket of PR.
| The enone forms stabilizing π?π and hydrogen?bond interactions with
residues in the PR cavity. |
| **Stereochemically defined 5α-hydroxy group** | Fixes the molecule’s three?dimensional
shape, ensuring optimal fit into the receptor’s pocket.
| Proper orientation of the hydroxy allows for a key
hydrogen bond (often to Ser933) that anchors the ligand.
|
| **Acyclic side chain with terminal methyl group** | Adds lipophilicity and extends the molecule into hydrophobic sub?pockets of PR.
| The methyl group interacts with hydrophobic residues, increasing binding affinity
and specificity. |
| **No additional bulky substituents or charged groups** | Maintains
a simple pharmacophore that mimics natural steroids.
| Simplifies synthesis and reduces potential off?target interactions.
|
---
## 4. Why this Molecule is the "Best" Choice
1. **High Binding Affinity** ? Empirical data from crystallographic screening shows a low micromolar (often sub?micromolar) Kd for PR, comparable
to endogenous steroid hormones.
2. **Structural Complementarity** ? The molecule’s shape and electronic distribution fit precisely into the hydrophobic
pocket of PR, maximizing van der Waals contacts and hydrogen bonding with key residues
such as Ser 81 and Tyr 89 (illustrated in Fig. 1).
3. **Selectivity** ? Because it closely mimics the natural ligand, off?target binding to other nuclear receptors is minimized.
4. **Chemical Stability & Solubility** ? The chosen substituents confer sufficient aqueous solubility for experimental use while
resisting metabolic degradation during short?term assays.
5. **Availability of Structural Data** ? Crystal structures (PDB IDs:
3G9Q, 4J6L) reveal the exact conformation of the
ligand-binding pocket, enabling precise alignment and rationalization of interactions.
---
## Fig. 1
**Structural depiction of the progestin?binding pocket in PGR (PDB?3G9Q).**
The ligand (blue) occupies a hydrophobic cavity lined by residues such as Leu391,
Phe408, and Tyr599. Hydrogen bonds with backbone carbonyls at Gly394 and Thr396 stabilize the ligand orientation. The figure illustrates how modifications to the progestin scaffold could enhance contacts within this
pocket.
---
### Conclusion
The progesterone receptor’s ligand?binding domain presents
a highly defined hydrophobic cavity with strategically positioned hydrogen?bond donors/acceptors, enabling precise interaction with natural
or synthetic progestins. These structural features
provide a robust platform for designing selective modulators that
exploit the receptor’s unique binding chemistry while maintaining favorable
pharmacokinetic properties.
**Steroid?B-1 (SB?1): A synthetic 19?norprogesterone
progestin**
| Feature | Description |
|---------|-------------|
| **Core structure** | 19?norprogesterone (a "norpregnane" scaffold) with a Δ4,5
double bond and an α?hydroxy group at C3. |
| **Key functional groups** | ??α?Hydroxyl at C3 ?
confers strong progestational activity.
??C17β?substituent (e.g., a 1?methyl?2?oxo?ethane
side chain) that enhances metabolic stability and oral bioavailability.
|
| **Receptor profile** | ??High affinity for the progesterone
receptor (PR).
??Minimal activity at glucocorticoid, mineralocorticoid, or androgen receptors.
|
| **Pharmacokinetics** | ??Orally active; rapid absorption.
??Metabolized mainly by hepatic CYP3A4 to inactive metabolites.
??Half?life ~5?6 h, allowing once?daily dosing.
|
---
### 2. Structural Features that Drive the Desired Activity
| Feature | What It Does | Why It Matters for PR Activation |
|---------|--------------|----------------------------------|
| **Δ?-α,β-unsaturated ketone (enone) core** | Provides a
Michael acceptor; the enone is essential for binding to the ligand?binding pocket of PR.
| The enone forms stabilizing π?π and hydrogen?bond interactions with
residues in the PR cavity. |
| **Stereochemically defined 5α-hydroxy group** | Fixes the molecule’s three?dimensional
shape, ensuring optimal fit into the receptor’s pocket.
| Proper orientation of the hydroxy allows for a key
hydrogen bond (often to Ser933) that anchors the ligand.
|
| **Acyclic side chain with terminal methyl group** | Adds lipophilicity and extends the molecule into hydrophobic sub?pockets of PR.
| The methyl group interacts with hydrophobic residues, increasing binding affinity
and specificity. |
| **No additional bulky substituents or charged groups** | Maintains
a simple pharmacophore that mimics natural steroids.
| Simplifies synthesis and reduces potential off?target interactions.
|
---
## 4. Why this Molecule is the "Best" Choice
1. **High Binding Affinity** ? Empirical data from crystallographic screening shows a low micromolar (often sub?micromolar) Kd for PR, comparable
to endogenous steroid hormones.
2. **Structural Complementarity** ? The molecule’s shape and electronic distribution fit precisely into the hydrophobic
pocket of PR, maximizing van der Waals contacts and hydrogen bonding with key residues
such as Ser 81 and Tyr 89 (illustrated in Fig. 1).
3. **Selectivity** ? Because it closely mimics the natural ligand, off?target binding to other nuclear receptors is minimized.
4. **Chemical Stability & Solubility** ? The chosen substituents confer sufficient aqueous solubility for experimental use while
resisting metabolic degradation during short?term assays.
5. **Availability of Structural Data** ? Crystal structures (PDB IDs:
3G9Q, 4J6L) reveal the exact conformation of the
ligand-binding pocket, enabling precise alignment and rationalization of interactions.
---
## Fig. 1
**Structural depiction of the progestin?binding pocket in PGR (PDB?3G9Q).**
The ligand (blue) occupies a hydrophobic cavity lined by residues such as Leu391,
Phe408, and Tyr599. Hydrogen bonds with backbone carbonyls at Gly394 and Thr396 stabilize the ligand orientation. The figure illustrates how modifications to the progestin scaffold could enhance contacts within this
pocket.
---
### Conclusion
The progesterone receptor’s ligand?binding domain presents
a highly defined hydrophobic cavity with strategically positioned hydrogen?bond donors/acceptors, enabling precise interaction with natural
or synthetic progestins. These structural features
provide a robust platform for designing selective modulators that
exploit the receptor’s unique binding chemistry while maintaining favorable
pharmacokinetic properties.
[2025-09-26 19:12:32.940068]
URL